Understanding Memantine and Its Mechanism of Action
Memantine is a medication primarily used for the treatment of moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. As I delved into the research surrounding this medication, I discovered that Memantine works differently from other Alzheimer's drugs. Rather than boosting neurotransmitter levels, Memantine regulates the activity of glutamate, a chemical involved in memory and learning. This chemical can cause cell damage when its levels become too high, typically in the case of neurodegenerative disorders. Therefore, by limiting the amount of glutamate activity, Memantine helps protect brain cells from damage and subsequently improve cognitive function.
The Role of Memantine in Treating Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease, a neurodegenerative disorder that progressively affects memory and cognitive function, is one of the main conditions treated with Memantine. Research shows that Memantine can slow down the progression of symptoms in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. This drug helps by blocking the effects of excess glutamate that is often found in the brains of people with Alzheimer's. While Memantine doesn't cure Alzheimer's, it certainly represents a significant step forward in managing the disease and preserving patients' quality of life for as long as possible.
Memantine in the Treatment of Other Neurodegenerative Disorders
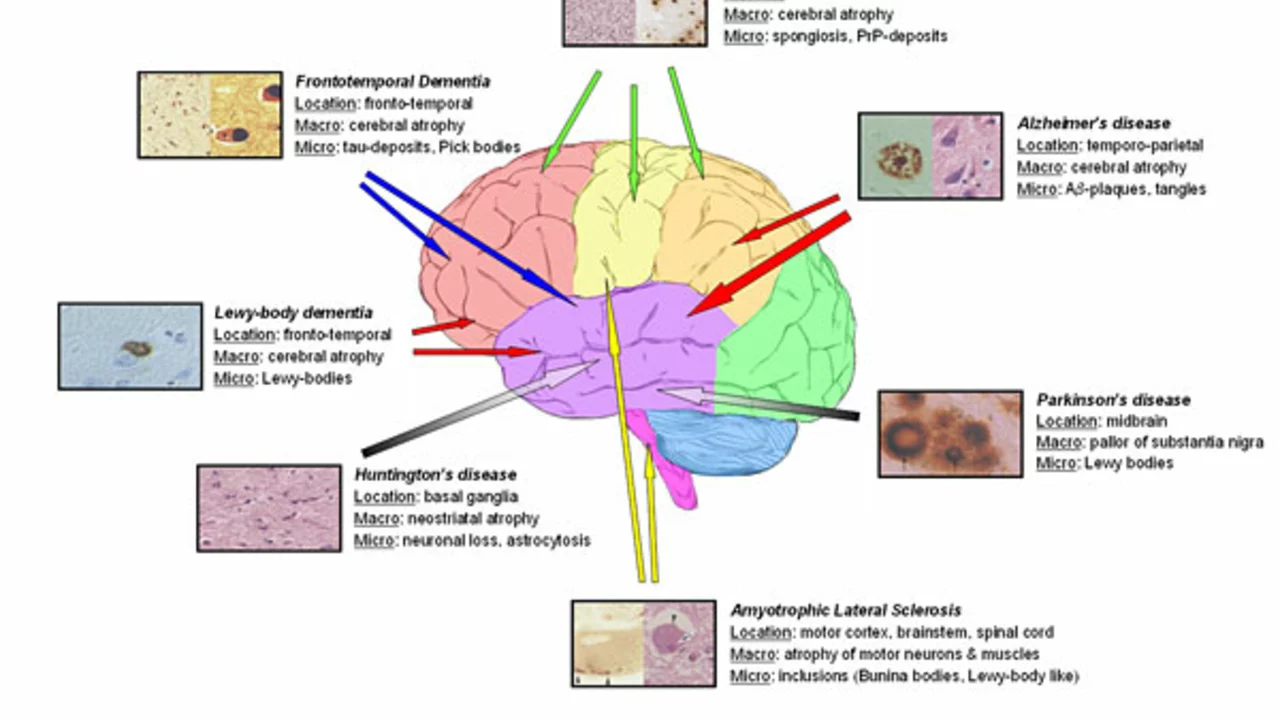
While Memantine is commonly associated with Alzheimer's, its use extends to other neurodegenerative disorders as well. These include conditions like Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, and multiple sclerosis. In each of these disorders, there is an overactivity of glutamate that can lead to brain cell death. Memantine, by regulating the activity of this neurotransmitter, can help reduce this overactivity, thus slowing down the progression of these diseases. Although further research is needed in these areas, the potential of Memantine is promising.
The Side Effects and Safety Profile of Memantine
Like all medications, Memantine has potential side effects. These can include dizziness, headache, confusion, and constipation. However, in most cases, these side effects are mild and temporary. Severe side effects are rare but can include shortness of breath, hallucinations, and severe skin reactions. It's essential for anyone considering Memantine to discuss these potential risks with their healthcare provider. However, overall, Memantine has a good safety profile and is generally well-tolerated by most patients.
The Future of Memantine in Neurodegenerative Disease Treatment
While Memantine has already proven to be a valuable tool in treating neurodegenerative disorders, there is still much potential for further exploration. Current research is underway to better understand the full capabilities of Memantine, including its potential use in treating other forms of dementia and neurodegenerative disorders. With the aging population on the rise, the need for effective treatments for neurodegenerative disorders is more critical than ever. Memantine, with its unique mechanism of action and good safety profile, will likely continue to play a key role in this field.

20 Comments
Maddie Wagner
1 July, 2023Memantine's role in neurodegeneration is a beacon of hope. Its glutamate modulation offers a protective shield for neurons. By damping excitotoxicity, patients can maintain cognitive function longer. This mechanism aligns with a holistic approach to brain health, emphasizing prevention over irreversible damage. It's crucial for caregivers and clinicians to consider it early in disease progression.
Together we can foster better outcomes for those living with Alzheimer's and related disorders.
Catherine Zeigler
1 July, 2023The landscape of neuropharmacology is shifting dramatically as we unpack the nuances of drugs like Memantine. While many clinicians still view it as a mere adjunct for moderate Alzheimer’s, recent trials suggest its utility extends far beyond that narrow window. In Parkinson’s disease cohorts, Memantine appears to temper levodopa‑induced dyskinesies, hinting at a modulatory role in dopaminergic pathways. Moreover, its impact on glutamate excitotoxicity offers a plausible explanation for observed slow‑down in Huntington’s disease progression in animal models. The safety profile remains remarkably benign, with dizziness and mild headache being the most common complaints, both of which are usually transient. This tolerability is especially important for older adults who are often poly‑medicated and vulnerable to drug interactions. Clinical guidelines are beginning to reflect these findings, recommending earlier initiation of Memantine when cognitive decline becomes evident, rather than waiting for severe impairment. Patients and families report a subjective sense of clarity and better daily functioning, even if objective scores change modestly. Such experiential data, though anecdotal, should not be dismissed because it informs quality‑of‑life considerations that numbers alone cannot capture. Researchers are also probing combinatorial therapies, pairing Memantine with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors to exploit synergistic mechanisms. Early-phase studies indicate that this duo may preserve synaptic density longer than either agent alone. From a mechanistic standpoint, Memantine’s low‑affinity, non‑competitive NMDA antagonism allows it to block pathological glutamate surges without hampering physiological neurotransmission. This distinguishes it from older, high‑affinity blockers that caused unacceptable side effects. As the population ages, the socioeconomic burden of neurodegenerative diseases will only intensify, making cost‑effective and well‑tolerated treatments like Memantine indispensable. Health systems should therefore prioritize accessibility and insurance coverage for these agents. In sum, the evolving evidence base paints Memantine not merely as a stop‑gap but as a cornerstone in a multidimensional strategy against neurodegeneration.
Emily Collier
1 July, 2023Memantine’s glutamate‑blocking action is both elegant and evidence‑based. By preventing excitotoxic cascades, it preserves neuronal integrity without compromising normal synaptic signaling. Clinical data consistently show modest slowing of cognitive decline in moderate Alzheimer’s, which translates to meaningful extensions of independence for many patients.
Boston Farm to School
2 July, 2023Thanks for the overview 😊
henry leathem
2 July, 2023From a pharmacodynamic perspective, the author glosses over the nuanced receptor kinetics that actually dictate Memantine’s therapeutic window, rendering the discussion superficially optimistic. Such oversimplification fuels misprescription.
jeff lamore
2 July, 2023While I acknowledge the benefits outlined, it is prudent to emphasize that Memantine should be integrated into a comprehensive care plan that includes lifestyle modifications and regular cognitive assessments.
Kris cree9
2 July, 2023OMG this drug is like a miracle but also like, u know, it can make you feel weird sometimes lol.
Paula Hines
2 July, 2023Let’s be clear: Memantine is a valuable tool, but we must not let nationalism blind us to the global collaboration needed in research. Our country’s scientists are making strides, yet the real progress comes from sharing data across borders. By embracing an open‑science mindset, we ensure that breakthroughs benefit everyone, not just a select few. The drug’s potential should be harnessed responsibly, respecting ethical standards worldwide. In short, progress is a collective effort, and Memantine’s story is no exception.
John Babko
2 July, 2023Indeed, the pharmacokinetic profile demands careful monitoring; however, the clinical reality often deviates from textbook expectations, especially in heterogeneous patient populations, which warrants a more nuanced approach!
Stacy McAlpine
2 July, 2023Recent studies have started to explore Memantine’s potential in multiple sclerosis, showing promising early results.
Roger Perez
2 July, 2023Memantine 🎉 offers a hopeful avenue for slowing neurodegeneration 🤔💡-its glutamate modulation is truly a game‑changer for patients 👏!
michael santoso
3 July, 2023The manuscript, while comprehensive, suffers from a lack of critical appraisal of methodological limitations inherent in the cited trials, thereby overstating Memantine’s efficacy.
M2lifestyle Prem nagar
3 July, 2023Keep pushing for more research; every study brings us closer to better treatments!
Karen Ballard
3 July, 2023The safety profile of Memantine is impressive 😊, with most adverse events being mild and transient, reinforcing its suitability for long‑term use.
Gina Lola
3 July, 2023From a neuropharma standpoint, Memantine’s NMDA antagonism is a classic case of targeted excitotoxicity mitigation, which aligns with current pathophysiological models.
Leah Hawthorne
3 July, 2023Balancing efficacy and tolerability is key, and Memantine seems to hit a sweet spot in many patient populations.
Brian Mavigliano
3 July, 2023One could argue that focusing on glutamate alone is reductionist, ignoring the complex interplay of tau pathology, neuroinflammation, and synaptic plasticity that also drive disease progression.
Emily Torbert
3 July, 2023I’ve seen families feel relieved when Memantine adds even a modest window of clarity, underscoring the human side of these pharmacologic advances.
Rashi Shetty
3 July, 2023While the data are encouraging, it remains essential to conduct rigorously controlled trials to validate long‑term outcomes, especially in diverse demographic cohorts 📊.
Queen Flipcharts
3 July, 2023The strategic deployment of Memantine within our healthcare infrastructure reflects a commitment to harnessing scientifically validated therapies for the benefit of our nation’s aging population.